字幕と単語
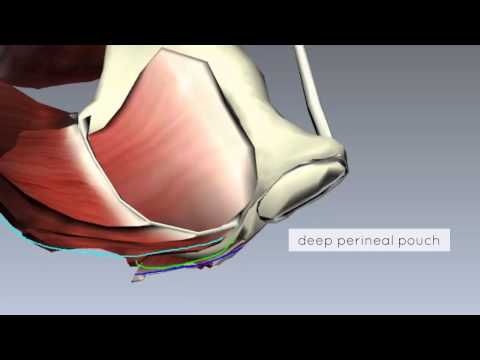
骨盤底パート2 - 腹膜と深部腹膜袋 - 3D解剖学チュートリアル (Pelvic Floor Part 2 - Perineal Membrane and Deep Perineal Pouch - 3D Anatomy Tutorial)
00
Juan が 2021 年 01 月 14 日 に投稿保存
動画の中の単語
content
US /ˈkɑnˌtɛnt/
・
UK /'kɒntent/
- adj.満足している;満足した
- n. (c./u.)内容;主題;コンテンツ;満足;コンテンツ;含有量
- v.t.満足させる
- v.i.同意する
A2 初級
もっと見る エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除
