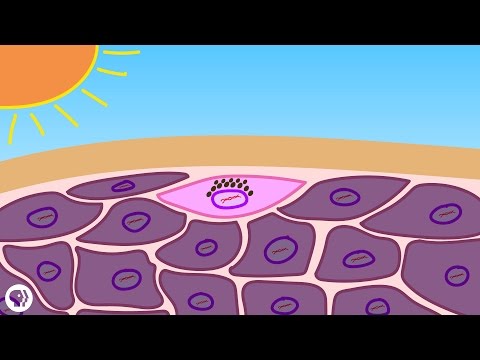
「紫外線」対策はなぜ必要?「日焼け」の仕組みを徹底解説!
Jack が 2023 年 08 月 23 日 に投稿  この条件に一致する単語はありません
この条件に一致する単語はありませんUS /ɪˈsenʃəli/
・
UK /ɪˈsenʃəli/
US /ˈprɛznt/
・
UK /'preznt/
- adj.出席している;現在
- n.プレゼント;現在時制;現在;贈り物
- v.t.紹介する;司会をする;発表する;提示する;(賞を)贈呈する
- v.i.現れる
- n. (c./u.)グロス(単位 : 1グロスは12ダース);合計;総重量
- v.t.総収益をあげる
- adj.気持ち悪い;総計の;下品な
US /ˈprɑːpərli/
・
UK /ˈprɔpəlɪ/
エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除