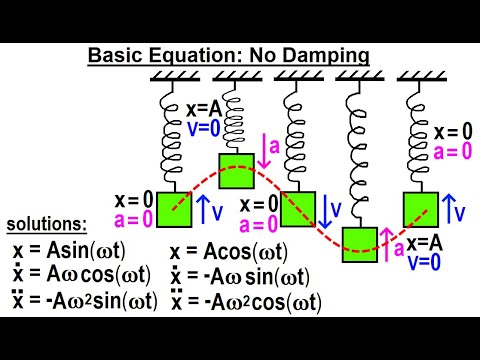
物理学Ch 16.1 減衰を伴う単純調和運動 (1 of 20) 基本方程式:減衰なし (Physics: Ch 16.1 Simple Harmonic Motion with Damping (1 of 20) Basic Equation: No Damping)
陳威諺 が 2024 年 10 月 20 日 に投稿  この条件に一致する単語はありません
この条件に一致する単語はありませんUS /ɪˈsenʃəli/
・
UK /ɪˈsenʃəli/
- v.t.(人を騙すために)ふりをする : 装う;仮定する : 推測する;(責任 : 任務などを)負う : 引き受ける
US /ˈkɑnstənt/
・
UK /'kɒnstənt/
US /ˈriəˌlaɪz/
・
UK /'ri:əlaɪz/
エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除