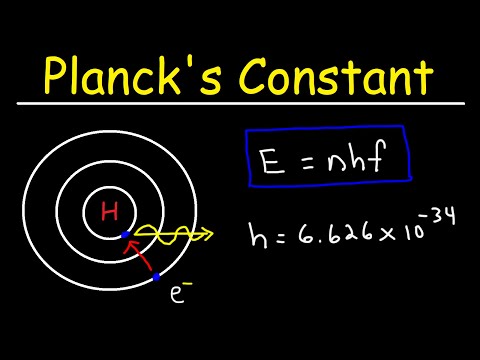
プランク定数と黒体放射 (Planck's Constant and BlackBody Radiation)
kevin が 2024 年 10 月 02 日 に投稿  この条件に一致する単語はありません
この条件に一致する単語はありませんUS /ɪˈvɛntʃuəli/
・
UK /ɪˈventʃuəli/
US /ˈmʌltəpəl/
・
UK /ˈmʌltɪpl/
- adj.複数の;多様な;多発性の;多重の
- n. (c.)倍数;多数;倍率
- pron.多数
US /ˈkɑnstənt/
・
UK /'kɒnstənt/
US /ˈnɛɡətɪv/
・
UK /'neɡətɪv/
- n.マイナスの電極;否定文の;「いや」という返事;写真や映画のネガ
- adj.嫌な;負の数の;悲観的な;否定的;陰性の;負の
エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除