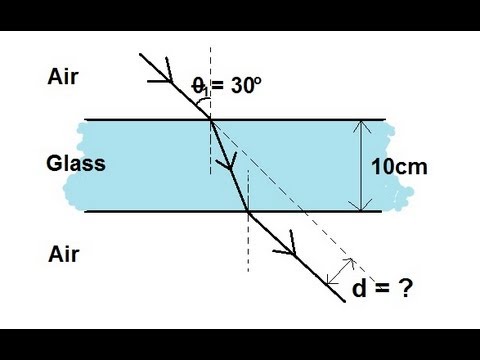
物理 52 屈折とスネルの法則(11の2) ガラス板を通過する光線 (Physics 52 Refraction and Snell's Law (2 of 11) Light Ray Going Through a Glass Slab)
kevin が 2024 年 10 月 02 日 に投稿  この条件に一致する単語はありません
この条件に一致する単語はありませんUS /sɪɡˈnɪfɪkənt/
・
UK /sɪgˈnɪfɪkənt/
- v.t./i.出場する;計算する;思う;思う
- n.姿 : 体形;数字;人物像;図表;著名人;姿の輪郭;数字
US /ˈslaɪtli/
・
UK /ˈslaɪtli/
エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除