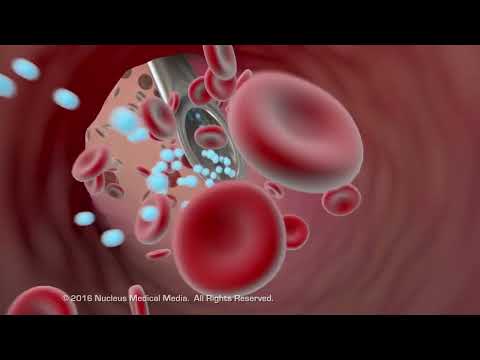
薬が体に吸収される仕組み (How Medications Get Absorbed By Your Body)
2hs2q6gy8d が 2024 年 06 月 20 日 に投稿  この条件に一致する単語はありません
この条件に一致する単語はありませんUS /ˈprɑsˌɛs, ˈproˌsɛs/
・
UK /prə'ses/
- v.t.(コンピュータの)データを処理する;処理する;処理する;一連の工程を経る;加工する : 加工処理する;理解する
- n. (c./u.)手続き;一連の行為;方法;訴訟手続き;プロセス (コンピューター)
- n. (c./u.)共有地;(地域共同体が所有する)共有地
- adj.公共の;典型的;一般の;広まっている;下品な;普通名詞の
US /ˈdʒɛnərəl/
・
UK /'dʒenrəl/
- adj.一般的な;大まかな;広範囲に適用できる;総司令官の
- n. (c.)大将
- n. (c./u.)一般大衆;一般的な研究分野
US /əˈmaʊnt/
・
UK /ə'maʊnt/
- n. (c./u.)量 : (金)額
- v.i.総計(いくらかに)達する
エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除