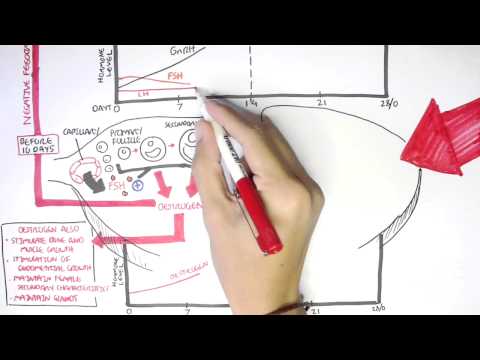
Female Reproductive System - Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Regulation
JillHuang が 2021 年 04 月 12 日 に投稿  この条件に一致する単語はありません
この条件に一致する単語はありませんUS /ɪˈsenʃəli/
・
UK /ɪˈsenʃəli/
US /ˈprɛznt/
・
UK /'preznt/
- adj.出席している;現在
- n.プレゼント;現在時制;現在;贈り物
- v.t.紹介する;司会をする;発表する;提示する;(賞を)贈呈する
- v.i.現れる
US /ˈtrɪɡɚ/
・
UK /'trɪɡə(r)/
- n.引き金;事を開始する装置;きっかけ;トラウマの引き金;トリガー (電子工学);トリガー (コンピュータ);トリガー (釣り)
- v.t.引き起こす;引き起こす;反射を引き起こす
エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除