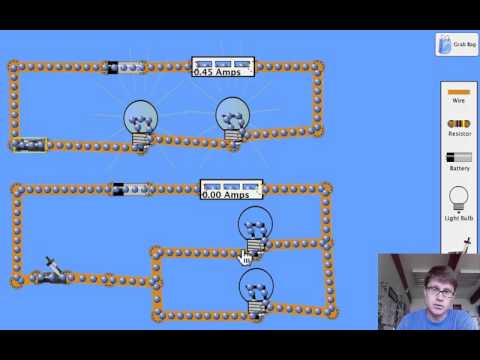
直列回路と並列回路 (Series and Parallel Circuits)
kiss08099 が 2021 年 01 月 14 日 に投稿  この条件に一致する単語はありません
この条件に一致する単語はありません- v.i.~歳になる;(変って)~になる : 変化する
- v.t./i.曲がる;向きを変える
- n.(道路の)曲がり角;(順番に回ってくる)担当 : 当番;順番;(予期せぬ突然の)変化
- v.t.(ものを)ろくろ(旋盤)にかけて作る
US /ˈkɚrənt, ˈkʌr-/
・
UK /'kʌrənt/
- n. (u.)電流;流れ;通貨
- adj.現在の;通用;最新
- n.傾向;世論
- n.落下距離;落下;減少;滴 : 一滴
- v.t.(途中で)降ろす;落とす;やめる;減らす;立ち寄る;下げる
- v.i.倒れる
US /ˈsɪriz/
・
UK /ˈsɪəri:z/
- n. (c./u.)連続;連続;シリーズ番組;シリーズ戦;級数;シリーズ
- n. pl.連続 : シリーズ
- adj.直列
エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除