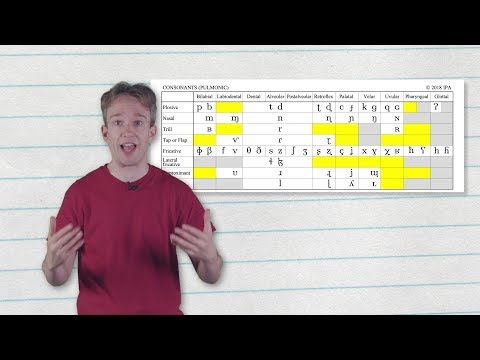
字幕と単語
存在するかもしれないが、存在しない言語の音 (The Language Sounds That Could Exist, But Don't)
00
林宜悉 が 2021 年 01 月 14 日 に投稿保存
動画の中の単語
shift
US /ʃɪft/
・
UK /ʃɪft/
- v.t./i.方向を変える;移動する;シフトする
- n. (c./u.)計画や意見を変えること;(交代制の)勤務時間;勤務時間;ワンピース;地殻変動;シフトキー;変速
- adj.シフトの : 交代勤務制の
A2 初級
もっと見る エネルギーを使用
すべての単語を解除
発音・解説・フィルター機能を解除
